This clinical investigation evaluates amniotic tissue and fluid allografts for chronic plantar fasciosis and Achilles tendinosis, demonstrating significant pain reduction without adverse effects.
This study introduces a novel Wharton’s jelly formulation and evaluates key regenerative components including growth factors, cytokines, hyaluronic acid, and extracellular vesicles.
This case report evaluates intra-articular Wharton’s jelly injection for knee osteoarthritis, demonstrating pain reduction, functional improvement, and favorable short-term clinical outcomes.
This clinical study evaluates allogeneic umbilical cord tissue injections, demonstrating reduced knee pain, improved physical function, and decreased reliance on pain medications.
This retrospective cohort study evaluates umbilical cord allograft use during revision carpal tunnel release, demonstrating improved long-term symptom relief and safety outcomes.
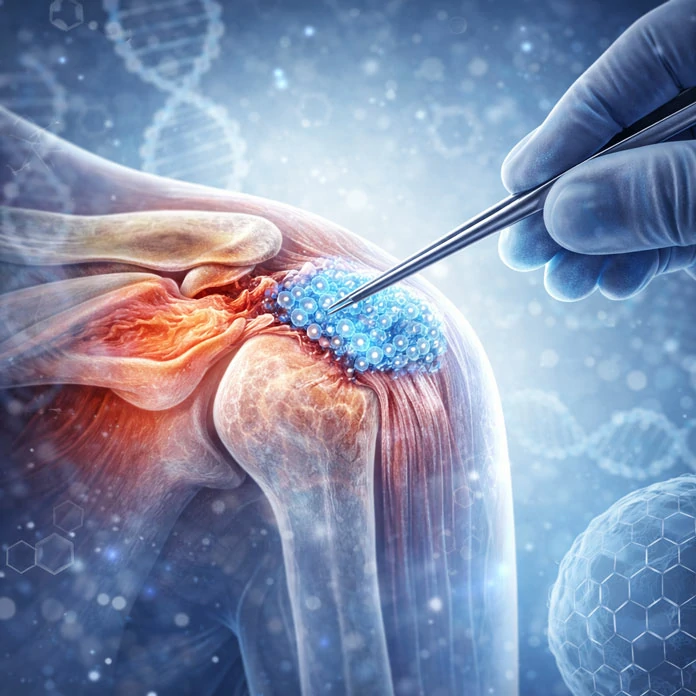
This case series investigates cryopreserved amniotic membrane and umbilical cord injections for partial rotator cuff tears, showing functional improvement without adverse events.
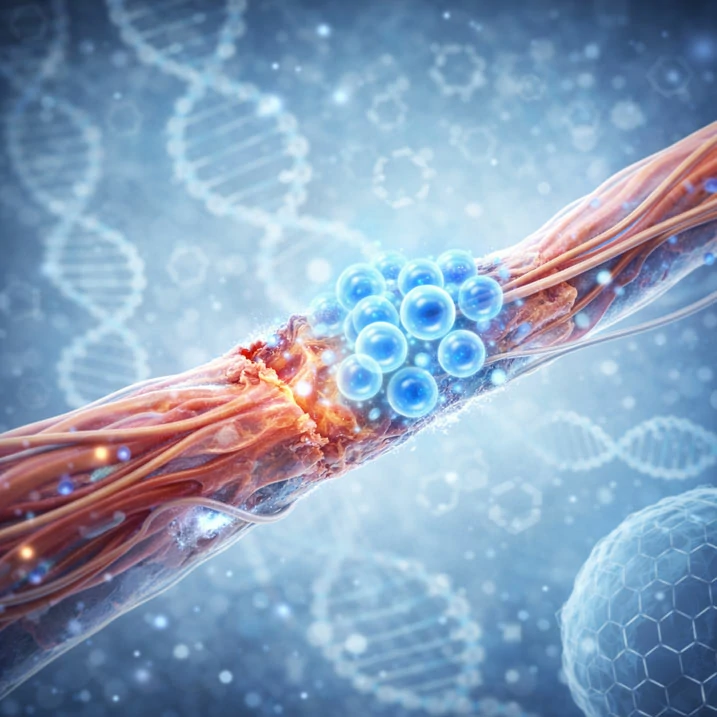
This study explores human umbilical cord–derived mesenchymal stem cells as a promising regenerative approach for peripheral nerve injury and functional recovery.
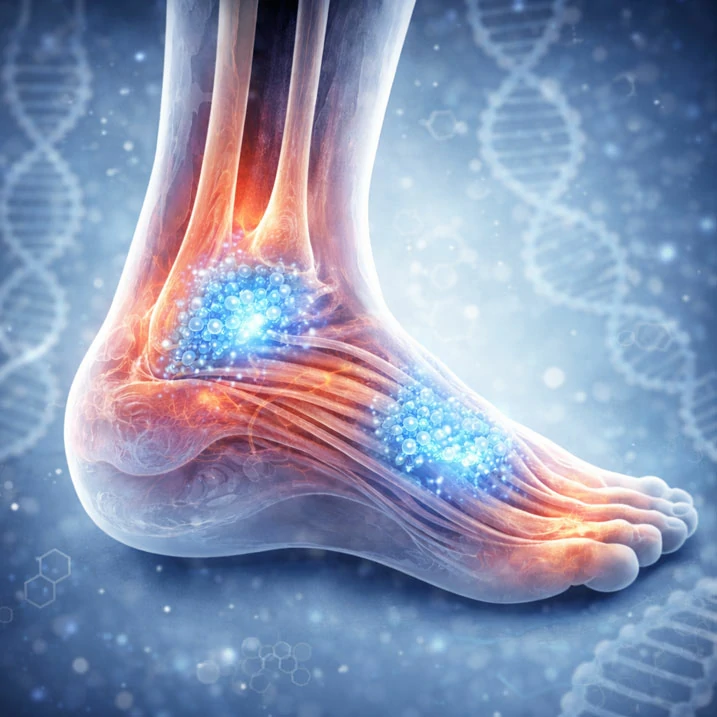
This clinical investigation evaluates amniotic tissue and fluid allografts for chronic plantar fasciosis and Achilles tendinosis, demonstrating significant pain reduction without adverse effects.
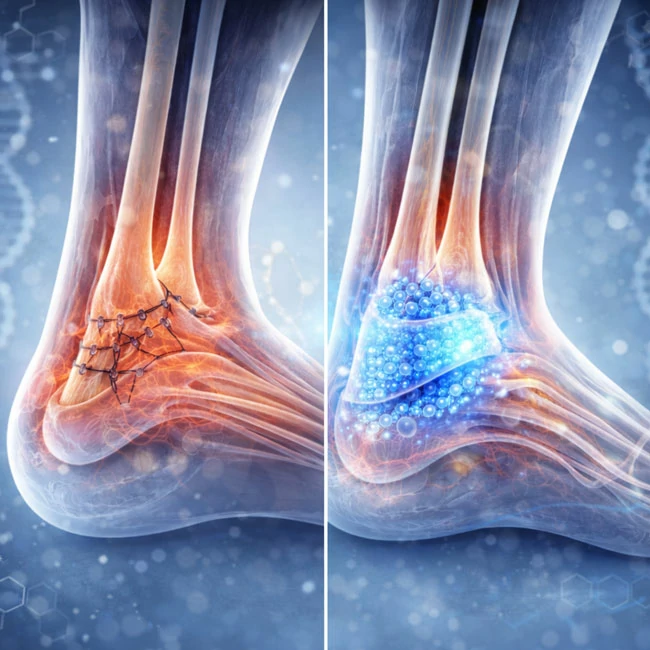
This comparative study reviews Achilles tendon repairs augmented with viable cryopreserved umbilical tissue, showing improved healing, reduced inflammation, and successful return to function.
This study reviews Achilles tendon rupture repairs augmented with viable cryopreserved umbilical tissue, highlighting enhanced surgical support and improved postoperative healing outcomes.
This review examines cartilage defect management, marrow stimulation techniques, and growth factors that promote cartilage regeneration and potentially slow osteoarthritis progression.
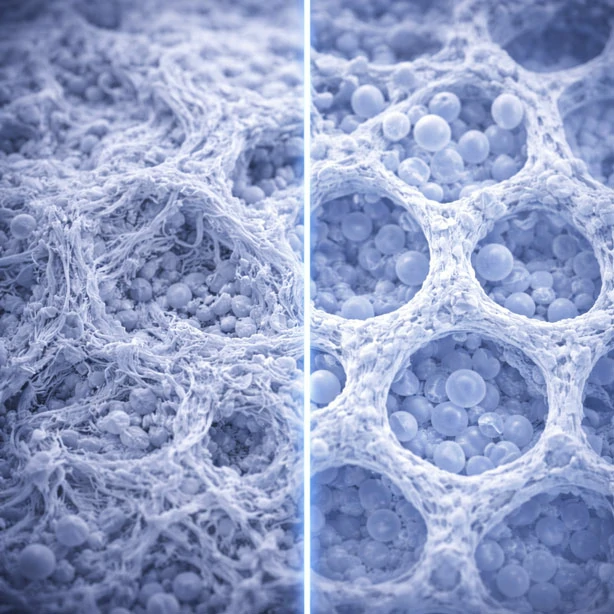
This study analyzes Wharton’s jelly structural matrices, demonstrating strong similarity to human cartilage and fascia, supporting its potential role in cartilage regeneration.